Neurofeedback
Learning Objectives
- Be able to explain what neurofeedback is
- Describe how EEG data are used in a neurofeedback system.
Neurofeedback is a kind of biofeedback. Biofeedback is a type of therapy where a practitioner uses sensors to measure body functions, with the goal of changing the results. It does this by finding and rewriting patterns. Positive or negative feedback is produced for desirable or undesirable brain activities, respectively. Neurofeedback usually provides audio and video feedback based on the positive or negative feed. This training of the brain teaches self-control of brain functions to subjects by measuring brain waves and providing a feedback signal (Marzbani et al., 2016). This allows the patient to learn how to self-regulate themself (Neuroelectrics, 2020).
One way that neurofeedback is tracked is through electroencephalography (EEG). Once an EEG is recorded, its various components are extracted and fed to subjects using an online feedback loop in the form of audio, video or a combination. As an illustration, the power of a signal in a frequency band can be shown by a varying bar graph. During this procedure, the subject becomes aware of the changes occurring during training and will be able to assess his/her progress in order to achieve optimum performance (Marzibaniet al., 2016). For example a subject might find a scene in a movie stressful, the EEG would detect that the person was stressed and would trigger the screen to darken or sound to cut out until the person was no longer feeling stressed.
Neurofeedback has many therapeutic uses such as helping: ADHD, autism, depression, anxiety, stress, insomnia, addictions. Neurofeedback is not a cure for many of these conditions. Still, neurofeedback can be an alternative to drug based medicine ways of helping people. It currently has a 60% success rate, but as a new type of therapy needs more testing for an accurate number (Haugg et al., 2021).
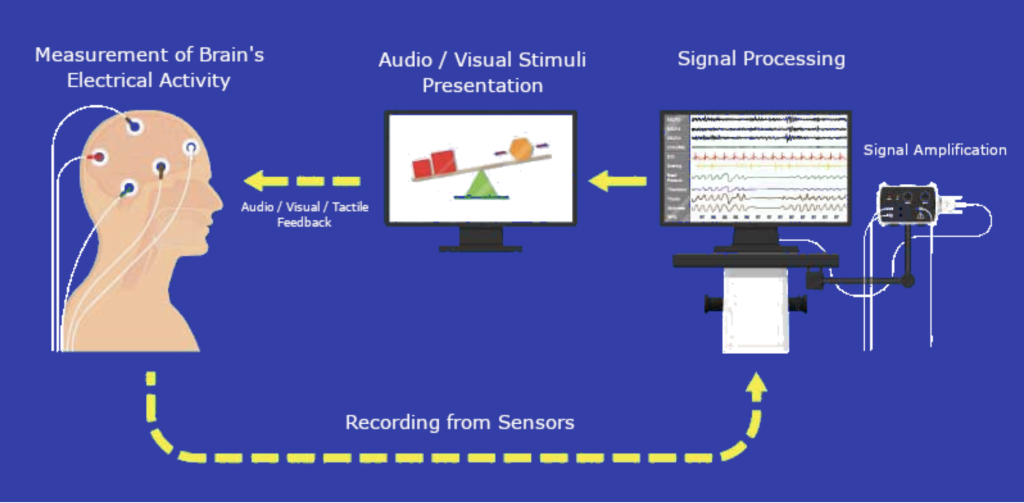
Marzbani H, Marateb HR, Mansourian M. Neurofeedback: A Comprehensive Review on System Design, Methodology and Clinical Applications. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2016 Apr;7(2):143-58. doi: 10.15412/J.BCN.03070208. PMID: 27303609; PMCID: PMC4892319. CC-BY-NC-3.0.
Neurofeedback, by Neuroelectrics. Accessed May 10, 2023. CC-BY-NC-SA.
Haugg, A., Renz, F. M., Nicholson, A. A., Lor, C., Götzendorfer, S. J., Sladky, R., … & Steyrl, D. (2021). Predictors of real-time fMRI neurofeedback performance and improvement–A machine learning mega-analysis. Neuroimage, 237, 118207. CC-BY.

