Indoor Air Pollution
In both developed and developing nations, indoor air pollution poses a greater health risk than outdoor air pollution. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and other agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), indoor air generally contains higher concentrations of toxic pollutants than outdoor air. Additionally, people generally spend more time indoors than outdoors, hence, the health effects from indoor air pollution in workplaces, schools, and homes are far greater than outdoors. Indoor pollution sources that release gases or particles into the air are the primary cause of indoor air quality problems in homes. Inadequate ventilation can increase indoor pollutant levels by not bringing in enough outdoor air to dilute emissions from indoor sources and by not carrying indoor air pollutants out of the home.
Outdoor air enters and leaves a building by infiltration, natural ventilation, and mechanical ventilation. In infiltration, outdoor air flows into the house through openings, joints, and cracks in walls, floors, and ceilings, and around windows and doors. In natural ventilation, air moves through opened windows and doors. Air movement associated with infiltration and natural ventilation is caused by air temperature differences between indoors and outdoors and by wind. Finally, there are a number of mechanical ventilation devices. These include outdoor-vented fans that intermittently remove air from a single room, and air handling systems that use fans and duct work to continuously remove indoor air and distribute filtered and conditioned outdoor air to strategic points throughout the house. The rate at which outdoor air replaces indoor air is described as the air exchange rate. When there is little infiltration, natural ventilation, or mechanical ventilation, the air exchange rate is low and pollutant levels can increase. High temperature and humidity levels can also increase concentrations of some pollutants.
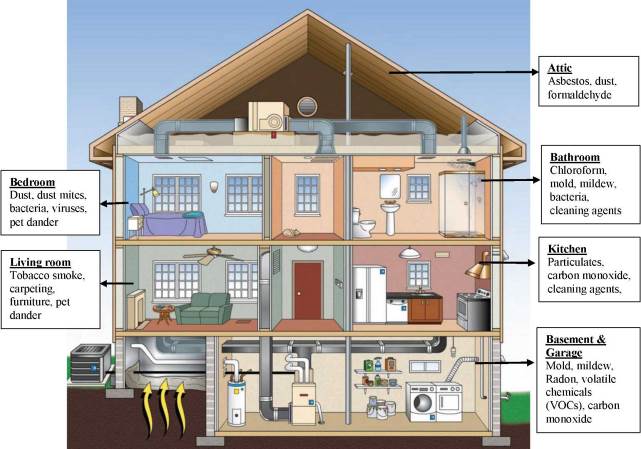
There are many sources of indoor air pollution in any home (Figure 6.11). These include combustion sources such as oil, gas, kerosene, coal, wood, and tobacco products; building materials and furnishings as diverse as deteriorated, asbestos-containing insulation, wet or damp carpet, and cabinetry or furniture made of certain pressed wood products; products for household cleaning and maintenance, personal care, or hobbies; central heating and cooling systems and humidification devices. Pollutants causing indoor air pollution can also originate from outside sources such as radon, pesticides, and outdoor air pollution. Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas produced from the decay of uranium in rock. If a building/home is constructed in an area with uranium containing rock, the gas can seep through the foundations and accumulate in basements. Exposure to radon can cause lung cancer.
The relative importance of any single source depends on how much of a given pollutant it emits and how hazardous those emissions are. In some cases, factors such as how old the source is and whether it is properly maintained are significant. For example, an improperly adjusted gas stove can emit significantly more carbon monoxide than one that is properly adjusted. Some sources, such as building materials, furnishings, and household products like air fresheners, release pollutants more or less continuously. Other sources, related to activities carried out in the home, release pollutants intermittently. These include smoking, the use of unvented or malfunctioning stoves, furnaces, or space heaters, the use of solvents in cleaning and hobby activities, the use of paint strippers in redecorating activities, and the use of cleaning products and pesticides in house-keeping. High pollutant concentrations can remain in the air for long periods after some of these activities.
Risks from indoor air pollution differ between less industrialized and industrialized nations. Indoor pollution has a greater impact in less industrialized nations where many people use cheaper sources of fuel such as wood, charcoal, and crop waste among others for cooking and heating, often with little or no ventilation. The most significant indoor pollutant, therefore, is soot and carbon monoxide. In industrialized nations, the primary indoor air health risks are cigarette smoke and radon.
Attribution
Zehnder, Caralyn; Manoylov, Kalina; Mutiti, Samuel; Mutiti, Christine; VandeVoort, Allison; and Bennett, Donna, “Introduction to Environmental Science: 2nd Edition” (2018). Biological Sciences Open Textbooks. 4.
https://oer.galileo.usg.edu/biology-textbooks/4
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 4.0 License.

