Cognition
Learning Objectives
Be able to give an example of a cognitive event.
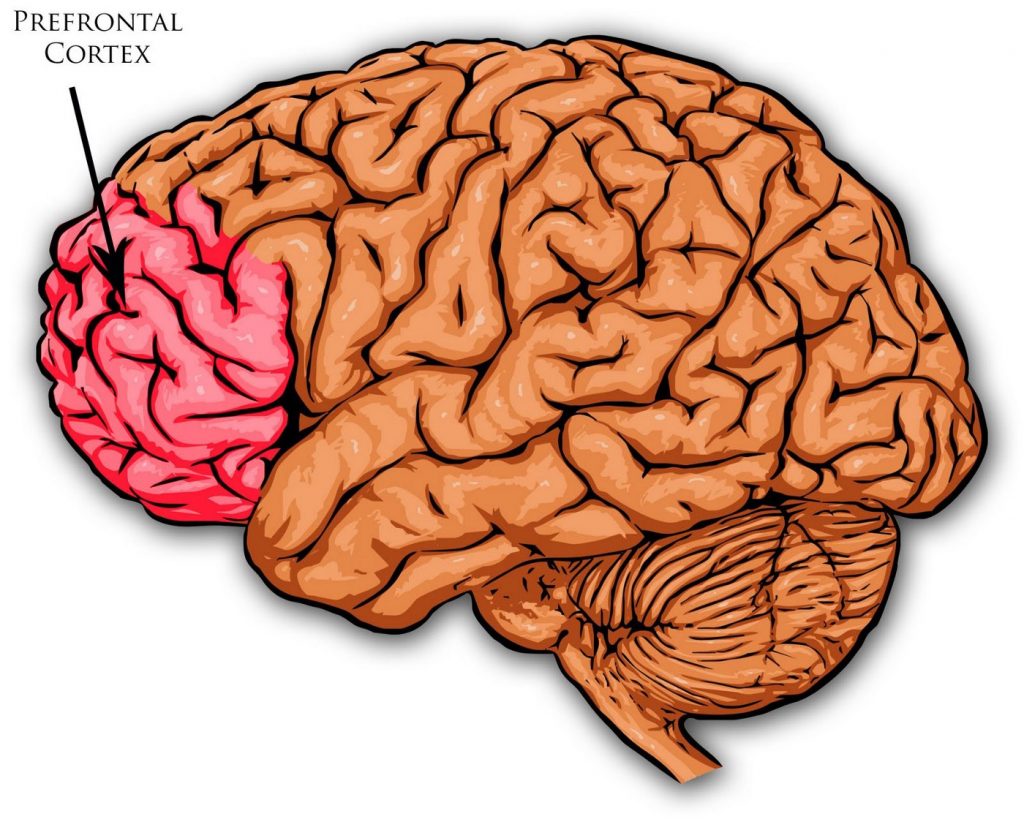
Know what part of your brain controls cognition.
One of the most important aspects of our daily lives is Cognition. Cognition is, as defined by merriam-webster, “of, relating to, being, or involving conscious intellectual activity (such as thinking, reasoning, or remembering)” there’s also a second definition stating “based on or capable of being reduced to empirical factual knowledge.” A side note, Empirical data is acquired through observation or experiences.
With these two definitions in mind, we’re able to conclude that a cognitive memory is one of past experiences or observations influencing the current state of mind, current reasoning, or thoughts about a situation or subject. Cognitive events are events that influence our thinking about something. Sadly, oftentimes these happen to be traumas.
Many people love animals. Dogs are looked at, by a majority of people, as a lovable companion. But, it’s possible that someone may have had a traumatic experience involving a dog attack for one example. It’s likely that this individual, if they haven’t processed and dealt with the event, now dislikes dogs, feeling intense anxiety when confronted with a dog. The same furry animal can come walking and two people can have completely opposite responses. This is just one example of a cognitive event. Specifically, how past experiences can influence your interpretation of a current situation.
There’s many interests regarding cognitive neuroscience and one of the main things studied, by observation, is memory distortion. This is known as “confabulation, in which patients with damage to various regions within the prefrontal cortex and related regions produce vivid but highly inaccurate ‘recollections’ of events that never happened.”
Another term to know is episodic memory, the system that enables people to recollect past experiences.
A major function of this system is “to draw on past experiences in a way that allows us to imagine and simulate episodes that might occur in our personal futures. Thinking about the future plays a critical role in mental life.” Looking back at the example of the dog you can see that this is exactly what happens. The person who went through the trauma foresees that event and simulates it to the present moment, while another person will foresee a loving animal.
Those that study brain function realize the important role of the frontal cortex in allowing individuals to anticipate or plan for the future. It is also said that “information about past experiences is useful only to the extent that it allows us to anticipate what may happen in the future.”
Our prefrontal cortex continues developing until around the age of 25. This area is important to many roles of mental health and our ability to comprehend the world, so make sure to take care of it!