10 Biotechnology
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
- Describe gel electrophoresis
- Explain molecular and reproductive cloning
- Describe biotechnology uses in medicine and agriculture
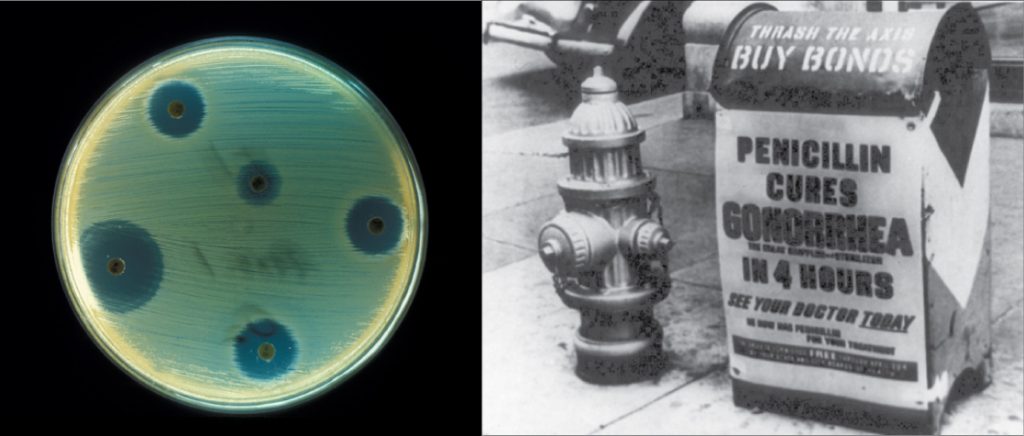
Biotechnology is the use of biological agents for technological advancement. Biotechnology was used for breeding livestock and crops long before people understood the scientific basis of these techniques. Since the discovery of the structure of DNA in 1953, the biotechnology field has grown rapidly through both academic research and private companies. The primary applications of this technology are in medicine (vaccine and antibiotic production) and agriculture (crop genetic modification in order to increase yields). Biotechnology also has many industrial applications, such as fermentation, treating oil spills, and producing biofuels (Figure 1).
Basic Techniques to Manipulate Genetic Material (DNA and RNA)
To understand the basic techniques used to work with nucleic acids, remember that nucleic acids are macromolecules made of nucleotides (a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base) linked by phosphodiester bonds. The phosphate groups on these molecules each have a net negative charge. An entire set of DNA molecules in the nucleus is called the genome. DNA has two complementary strands linked by hydrogen bonds between the paired bases. Exposure to high temperatures (DNA denaturation) can separate the two strands and cooling can reanneal them. The DNA polymerase enzyme can replicate the DNA. Unlike DNA, which is located in the eukaryotic cells’ nucleus, RNA molecules leave the nucleus. The most common type of RNA that researchers analyze is the messenger RNA (mRNA) because it represents the protein-coding genes that are actively expressed. However, RNA molecules present some other challenges to analysis, as they are often less stable than DNA.
DNA and RNA Extraction
To study or manipulate nucleic acids, one must first isolate or extract the DNA or RNA from the cells. Researchers use various techniques to extract different types of DNA (Figure 2). Most nucleic acid extraction techniques involve steps to break open the cell and use enzymatic reactions to destroy all macromolecules that are not desired (such as unwanted molecule degradation and separation from the DNA sample). A lysis buffer (a solution which is mostly a detergent) breaks cells. Note that lysis means “to split”. These enzymes break apart lipid molecules in the cell membranes and nuclear membranes. Enzymes such as proteases that break down proteins inactivate macromolecules, and ribonucleases (RNAses) that break down RNA. Using alcohol precipitates the DNA. Human genomic DNA is usually visible as a gelatinous, white mass. One can store the DNA samples frozen at –80°C for several years.
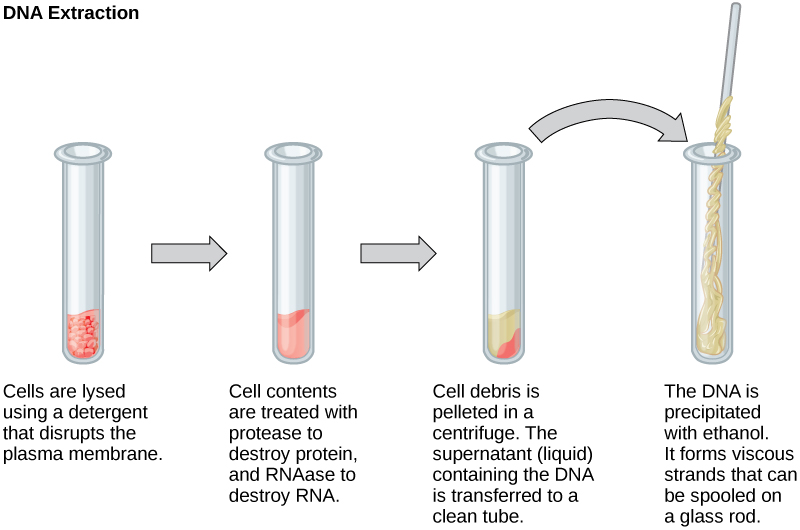
Scientists perform RNA analysis to study gene expression patterns in cells. RNA is naturally very unstable because RNAses are commonly present in nature and very difficult to inactivate. Similar to DNA, RNA extraction involves using various buffers and enzymes to inactivate macromolecules and preserve the RNA.
Gel Electrophoresis
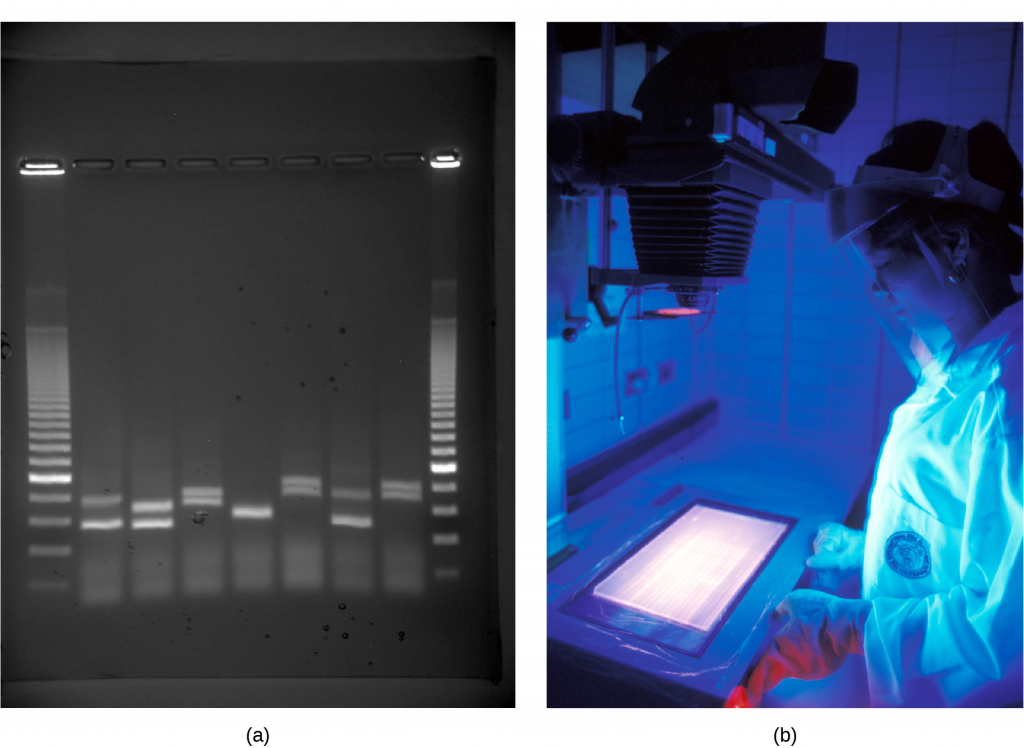
Because nucleic acids are negatively charged ions at neutral or basic pH in an aqueous environment, an electric field can mobilize them. Gel electrophoresis is a technique that scientists use to separate molecules on the basis of size, using this charge. One can separate the nucleic acids as whole chromosomes or fragments. The nucleic acids load into a slot near the semisolid, porous gel matrix’s negative electrode, and pulled toward the positive electrode at the gel’s opposite end. Smaller molecules move through the gel’s pores faster than larger molecules. This difference in the migration rate separates the fragments on the basis of size. There are molecular weight standard samples that researchers can run alongside the molecules to provide a size comparison. We can observe nucleic acids in a gel matrix using various fluorescent or colored dyes. Distinct nucleic acid fragments appear as bands at specific distances from the gel’s top (the negative electrode end) on the basis of their size (Figure 3). A mixture of genomic DNA fragments of varying sizes appear as a long smear; whereas, uncut genomic DNA is usually too large to run through the gel and forms a single large band at the gel’s top.
Nucleic Acid Fragment Amplification by Polymerase Chain Reaction
Although genomic DNA is visible to the naked eye when it is extracted in bulk, DNA analysis often requires focusing on one or more specific genome regions. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that scientists use to amplify specific DNA regions for further analysis (Figure 4). Researchers use PCR for many purposes in laboratories, such as cloning gene fragments to analyze genetic diseases, identifying contaminant foreign DNA in a sample, and amplifying DNA for sequencing. More practical applications include determining paternity and detecting genetic diseases.
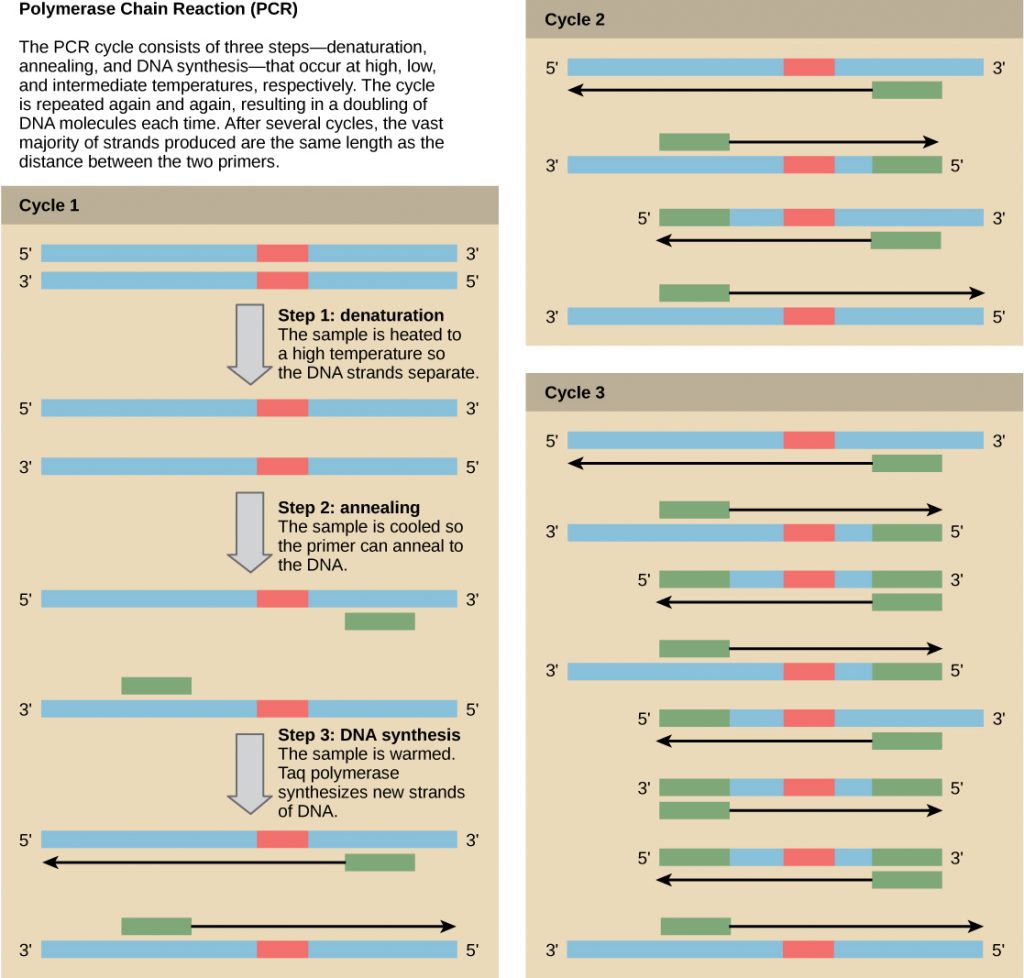
DNA fragments can also be amplified from an RNA template in a process called reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR). The first step is to recreate the original DNA template strand (called cDNA) by applying DNA nucleotides to the mRNA. This process is called reverse transcription. This requires the presence of an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. After the cDNA is made, regular PCR can be used to amplify it.
Hybridization, Southern Blotting, and Northern Blotting
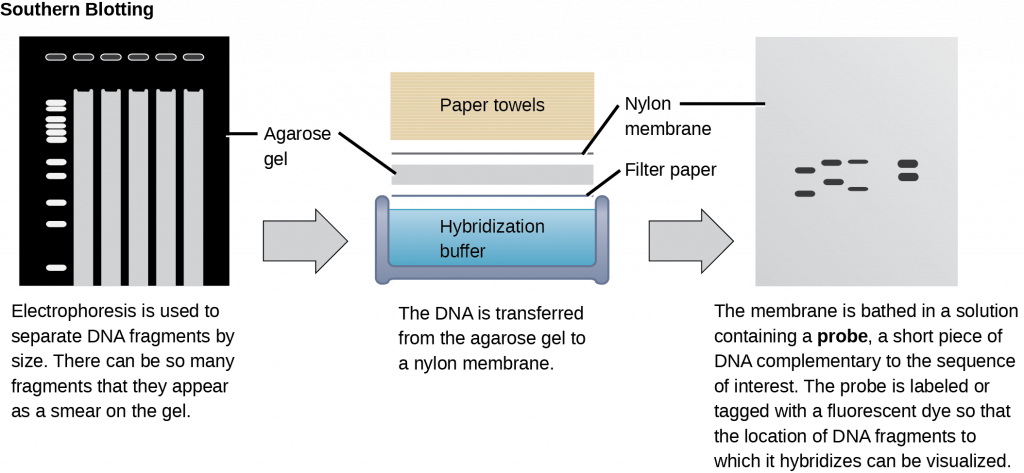
Scientists can probe nucleic acid samples, such as fragmented genomic DNA and RNA extracts, for the presence of certain sequences. Scientists design and label short DNA fragments, or probes with radioactive or fluorescent dyes to aid detection. Gel electrophoresis separates the nucleic acid fragments according to their size. Scientists then transfer the fragments in the gel onto a nylon membrane in a procedure we call blotting (Figure 5). Scientists can then probe the nucleic acid fragments that are bound to the membrane’s surface with specific radioactively or fluorescently labeled probe sequences. When scientists transfer DNA to a nylon membrane, they refer to the technique as Southern blotting. When they transfer the RNA to a nylon membrane, they call it Northern blotting. Scientists use Southern blots to detect the presence of certain DNA sequences in a given genome, and Northern blots to detect gene expression.
Molecular Cloning
In general, the word “cloning” means the creation of a perfect replica; however, in biology, the re-creation of a whole organism is referred to as “reproductive cloning.” Long before attempts were made to clone an entire organism, researchers learned how to reproduce desired regions or fragments of the genome, a process that is referred to as molecular cloning.
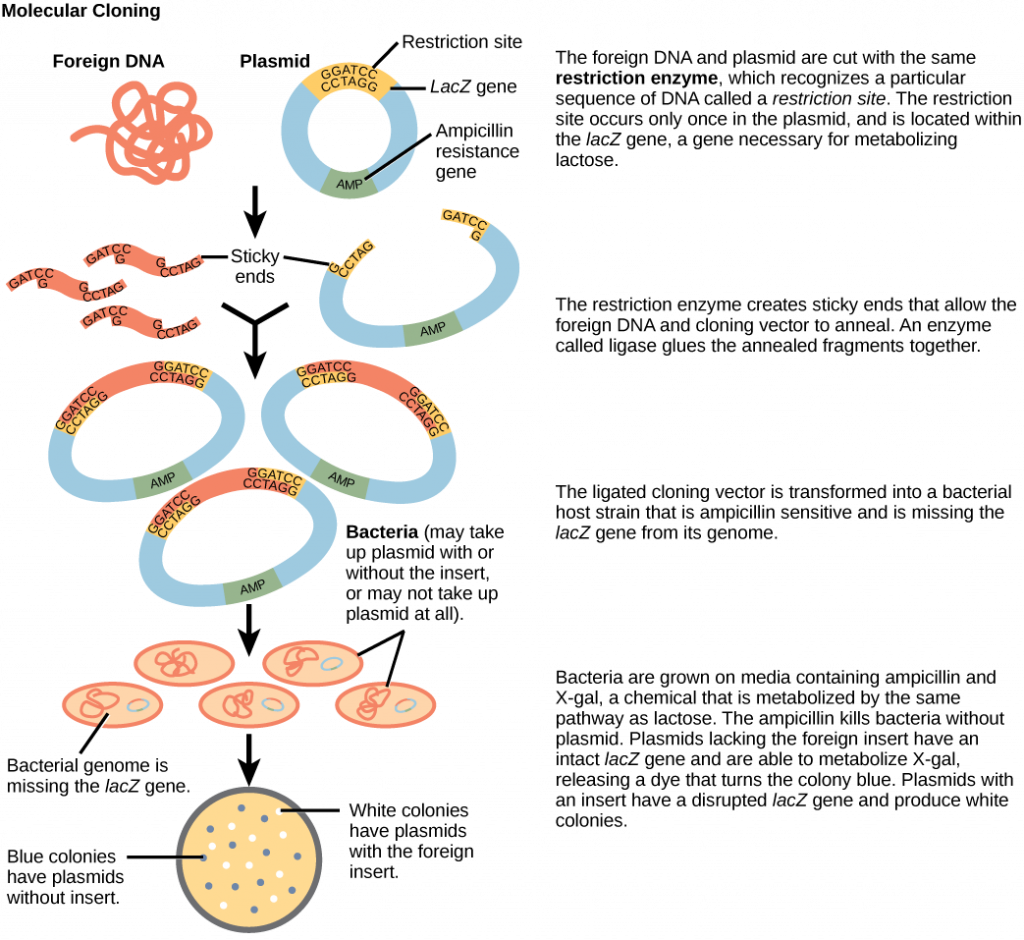
Cloning small genome fragments allows researchers to manipulate and study specific genes (and their protein products), or noncoding regions in isolation. A plasmid, or vector, is a small circular DNA molecule that replicates independently of the chromosomal DNA. In cloning, scientists can use the plasmid molecules to provide a “folder” in which to insert a desired DNA fragment. Plasmids are usually introduced into a bacterial host for proliferation. In the bacterial context, scientists call the DNA fragment from the human genome (or the genome of another studied organism) foreign DNA, or a transgene, to differentiate it from the bacterium’s DNA, or the host DNA.
Plasmids occur naturally in bacterial populations (such as Escherichia coli) and have genes that can contribute favorable traits to the organism, such as antibiotic resistance (the ability to be unaffected by antibiotics). Scientists have repurposed and engineered plasmids as vectors for molecular cloning and the large-scale production of important reagents, such as insulin and human growth hormone. An important feature of plasmid vectors is the ease with which scientists can introduce a foreign DNA fragment via the multiple cloning site (MCS). The MCS is a short DNA sequence containing multiple sites that different commonly available restriction endonucleases can cut. Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences and cut them in a predictable manner. They are naturally produced by bacteria as a defense mechanism against foreign DNA. Many restriction endonucleases make staggered cuts in the two DNA strands, such that the cut ends have a 2- or 4-base single-stranded overhang. Because these overhangs are capable of annealing with complementary overhangs, we call them “sticky ends.” Adding the enzyme DNA ligase permanently joins the DNA fragments via phosphodiester bonds. In this way, scientists can splice any DNA fragment generated by restriction endonuclease cleavage between the plasmid DNA’s two ends that has been cut with the same restriction endonuclease (Figure 6).
Recombinant DNA Molecules
Plasmids with foreign DNA inserted into them are called recombinant DNA molecules because they are created artificially and do not occur in nature. They are also called chimeric molecules because the origin of different molecule parts of the molecules can be traced back to different species of biological organisms or even to chemical synthesis. We call proteins that are expressed from recombinant DNA molecules recombinant proteins. Not all recombinant plasmids are capable of expressing genes. The recombinant DNA may need to move into a different vector (or host) that is better designed for gene expression. Scientists may also engineer plasmids to express proteins only when certain environmental factors stimulate them, so they can control the recombinant proteins’ expression.
VISUAL CONNECTION
You are working in a molecular biology lab and, unbeknownst to you, your lab partner left the foreign genomic DNA that you are planning to clone on the lab bench overnight instead of storing it in the freezer. As a result, it was degraded by nucleases, but still used in the experiment. The plasmid, on the other hand, is fine. What results would you expect from your molecular cloning experiment?
- There will be no colonies on the bacterial plate.
- There will be blue colonies only.
- There will be blue and white colonies.
- There will be white colonies only.
Answer:
You’d expect the experiment would result in blue colonies only. (b.)
Cellular Cloning
Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and yeast, naturally produce clones of themselves when they replicate asexually by binary fission; this is known as cellular cloning. The nuclear DNA duplicates by the process of mitosis, which creates an exact replica of the genetic material.
Reproductive Cloning
Reproductive cloning is a method scientists use to clone or identically copy an entire multicellular organism. Most multicellular organisms undergo reproduction by sexual means, which involves genetic hybridization of two individuals (parents), making it impossible to generate an identical copy or a clone of either parent. Recent advances in biotechnology have made it possible to artificially induce mammal asexual reproduction in the laboratory.
Parthenogenesis, or “virgin birth,” occurs when an embryo grows and develops without egg fertilization. This is a form of asexual reproduction. An example of parthenogenesis occurs in species in which the female lays an egg and if the egg is fertilized, it is a diploid egg and the individual develops into a female. If the egg is not fertilized, it remains a haploid egg and develops into a male. The unfertilized egg is a parthenogenic, or virgin egg. Some insects and reptiles lay parthenogenic eggs that can develop into adults.
Sexual reproduction requires two cells. When the haploid egg and sperm cells fuse, a diploid zygote results. The zygote nucleus contains the genetic information to produce a new individual. However, early embryonic development requires the cytoplasmic material contained in the egg cell. This idea forms the basis for reproductive cloning. Therefore, if we replace the egg cell’s haploid nucleus with a diploid nucleus from the cell of any individual of the same species (a donor), it will become a zygote that is genetically identical to the donor. Somatic cell nuclear transfer is the technique of transferring a diploid nucleus into an enucleated egg. Scientists can use it for either therapeutic cloning or reproductive cloning.
The first cloned animal was Dolly, a sheep born in 1996. The reproductive cloning success rate at the time was very low. Dolly lived for seven years and died of respiratory complications (Figure 7). There is speculation that because the cell DNA belongs to an older individual, DNA’s age may affect a cloned individual’s life expectancy. Since Dolly, scientists have cloned successfully several animals such as horses, bulls, and goats, although these animals often exhibit facial, limb, and cardiac abnormalities. There have been attempts at producing cloned human embryos as sources of embryonic stem cells for therapeutic purposes. Therapeutic cloning produces stem cells in the attempt to remedy detrimental diseases or defects (unlike reproductive cloning, which aims to reproduce an organism). Still, some have met therapeutic cloning efforts with resistance because of bioethical considerations.
VISUAL CONNECTION
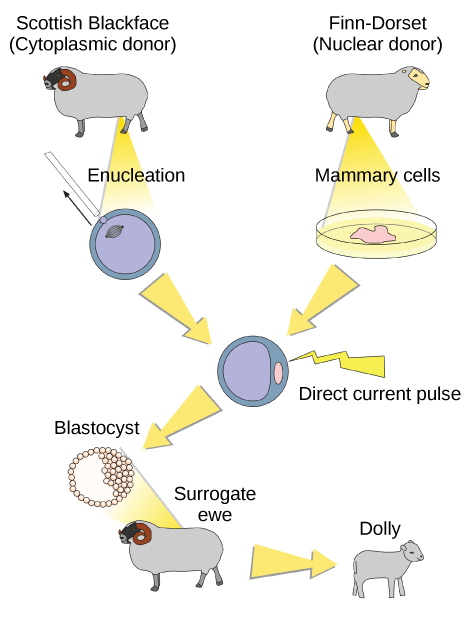
Do you think Dolly was a Finn-Dorset or a Scottish Blackface sheep?
Answer:
Dolly was a Finn-Dorset sheep because even though the original cell came from a Scottish blackface sheep and the surrogate mother was a Scottish blackface, the DNA came from a Finn-Dorset.
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering is the alteration of an organism’s genotype using recombinant DNA technology to modify an organism’s DNA to achieve desirable traits. The addition of foreign DNA in the form of recombinant DNA vectors generated by molecular cloning is the most common method of genetic engineering. The organism that receives the recombinant DNA is a genetically modified organism (GMO). If the foreign DNA comes from a different species, the host organism is transgenic. Scientists have genetically modified bacteria, plants, and animals since the early 1970s for academic, medical, agricultural, and industrial purposes. In the US, GMOs such as Roundup-ready soybeans and borer-resistant corn are part of many common processed foods.
Gene Targeting
Although classical methods of studying gene function began with a given phenotype and determined the genetic basis of that phenotype, modern techniques allow researchers to start at the DNA sequence level and ask: “What does this gene or DNA element do?” This technique, reverse genetics, has resulted in reversing the classic genetic methodology. This method would be similar to damaging a body part to determine its function. An insect that loses a wing cannot fly, which means that the wing’s function is flight. The classical genetic method would compare insects that cannot fly with insects that can fly, and observe that the non-flying insects have lost wings. Similarly, mutating or deleting genes provides researchers with clues about gene function. We collectively call the methods they use to disable gene function gene targeting. Gene targeting is the use of recombinant DNA vectors to alter a particular gene’s expression, either by introducing mutations in a gene, or by eliminating a certain gene’s expression by deleting a part or all of the gene sequence from the organism’s genome.
Biotechnology in Medicine and Agriculture
It is easy to see how biotechnology can be used for medicinal purposes. Knowledge of the genetic makeup of our species, the genetic basis of heritable diseases, and the invention of technology to manipulate and fix mutant genes provides methods to treat the disease. Biotechnology in agriculture can enhance resistance to disease, pest, and environmental stress, and improve both crop yield and quality.
Genetic Diagnosis and Gene Therapy
Scientists call the process of testing for suspected genetic defects before administering treatment genetic diagnosis by genetic testing. Depending on the inheritance patterns of a disease-causing gene, family members are advised to undergo genetic testing. For example, doctors usually advise women diagnosed with breast cancer to have a biopsy so that the medical team can determine the genetic basis of cancer development. Doctors base treatment plans on genetic test findings that determine the type of cancer. If inherited gene mutations cause the cancer, doctors also advise other female relatives to undergo genetic testing and periodic screening for breast cancer. Doctors also offer genetic testing for fetuses (or embryos with in vitro fertilization) to determine the presence or absence of disease-causing genes in families with specific debilitating diseases.
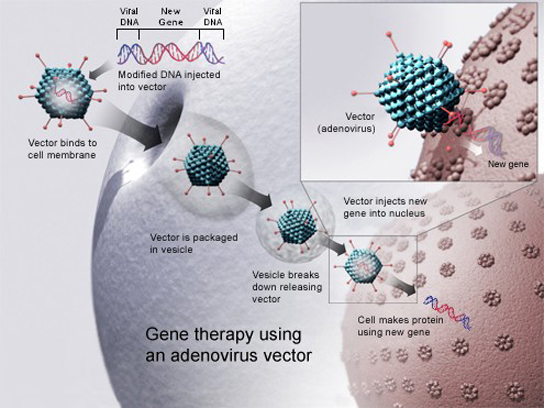
Gene therapy is a genetic engineering technique used to cure disease. In its simplest form, it involves the introduction of a good gene at a random location in the genome to aid the cure of a disease that is caused by a mutated gene. The good gene is usually introduced into diseased cells as part of a vector transmitted by a virus that can infect the host cell and deliver the foreign DNA (Figure 8). More advanced forms of gene therapy try to correct the mutation at the original site in the genome, such as is the case with treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
Production of Vaccines, Antibiotics, and Hormones
Traditional vaccination strategies use weakened or inactive forms of microorganisms to mount the initial immune response. Modern techniques use the genes of microorganisms cloned into vectors to mass produce the desired antigen. Doctors then introduce the antigen into the body to stimulate the primary immune response and trigger immune memory. The medical field has used genes cloned from the influenza virus to combat the constantly changing strains of this virus.
Antibiotics are a biotechnological product. Microorganisms, such as fungi, naturally produce them to attain an advantage over bacterial populations. Cultivating and manipulating fungal cells produces antibodies.
Scientists used recombinant DNA technology to produce large-scale quantities of human insulin in E. coli as early as 1978. Previously, it was only possible to treat diabetes with pig insulin, which caused allergic reactions in humans because of differences in the gene product. In addition, doctors use human growth hormone (HGH) to treat growth disorders in children. Researchers cloned the HGH gene from a cDNA library and inserted it into E. coli cells by cloning it into a bacterial vector.
Transgenic Animals
Although several recombinant proteins in medicine are successfully produced in bacteria, some proteins require a eukaryotic animal host for proper processing. For this reason, the desired genes are cloned and expressed in animals, such as sheep, goats, chickens, and mice. We call animals that have been modified to express recombinant DNA transgenic animals. Several human proteins are expressed in transgenic sheep and goat milk, and some are expressed in chicken eggs. Scientists have used mice extensively for expressing and studying recombinant gene and mutation effects.
Transgenic Plants
Manipulating the DNA of plants (i.e., creating GMOs) has helped to create desirable traits, such as disease resistance, herbicide and pesticide resistance, better nutritional value, and better shelf-life (Figure 9). Plants are the most important source of food for the human population. Farmers developed ways to select for plant varieties with desirable traits long before modern-day biotechnology practices were established.

We call plants that have received recombinant DNA from other species transgenic plants. Because they are not natural, government agencies closely monitor transgenic plants and other GMOs to ensure that they are fit for human consumption and do not endanger other plant and animal life. Because foreign genes can spread to other species in the environment, extensive testing is required to ensure ecological stability. Staples like corn, potatoes, and tomatoes were the first crop plants that scientists genetically engineered.
Transformation of Plants Using Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Gene transfer occurs naturally between species in microbial populations. Many viruses that cause human diseases, such as cancer, act by incorporating their DNA into the human genome. In plants, tumors caused by the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens occur by DNA transfer from the bacterium to the plant. Although the tumors do not kill the plants, they stunt the plants and they become more susceptible to harsh environmental conditions. A. tumefaciens affects many plants such as walnuts, grapes, nut trees, and beets. Artificially introducing DNA into plant cells is more challenging than in animal cells because of the thick plant cell wall.
Researchers used the natural transfer of DNA from Agrobacterium to a plant host to introduce DNA fragments of their choice into plant hosts. In nature, the disease-causing A. tumefaciens have a set of plasmids, Ti plasmids (tumor-inducing plasmids), that contain genes to produce tumors in plants. DNA from the Ti plasmid integrates into the infected plant cell’s genome. Researchers manipulate the Ti plasmids to remove the tumor-causing genes and insert the desired DNA fragment for transfer into the plant genome. The Ti plasmids carry antibiotic resistance genes to aid selection and researchers can propagate them in E. coli cells as well.
The Organic Insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a bacterium that produces protein crystals during sporulation that are toxic to many insect species that affect plants. Insects need to ingest Bt toxin in order to activate the toxin. Insects that have eaten Bt toxin stop feeding on the plants within a few hours. After the toxin activates in the insects’ intestines, they die within a couple of days. Modern biotechnology has allowed plants to encode their own crystal Bt toxin that acts against insects. Scientists have cloned the crystal toxin genes from Bt and introduced them into plants. Bt toxin is safe for the environment, nontoxic to humans and other mammals, and organic farmers have approved it as a natural insecticide.
Flavr Savr Tomato
The first GM crop on the market was the Flavr Savr Tomato in 1994. Scientists used antisense RNA technology to slow the softening and rotting process caused by fungal infections, which led to increased shelf life of the GM tomatoes. Additional genetic modification improved the tomato’s flavor. The Flavr Savr tomato did not successfully stay in the market because of problems maintaining and shipping the crop.
Glossary
- antibiotic resistance
- ability of an organism to be unaffected by an antibiotic’s actions
- biotechnology
- use of biological agents for technological advancement
- cellular cloning
- production of identical cell populations by binary fission
- clone
- exact replica
- foreign DNA
- DNA that belongs to a different species or DNA that is artificially synthesized
- gel electrophoresis
- technique used to separate molecules on the basis of size using electric charge
- gene targeting
- method for altering the sequence of a specific gene by introducing the modified version on a vector
- gene therapy
- technique used to cure inheritable diseases by replacing mutant genes with good genes
- genetic diagnosis
- diagnosis of the potential for disease development by analyzing disease-causing genes
- genetic engineering
- alteration of the genetic makeup of an organism
- genetic testing
- process of testing for the presence of disease-causing genes
- genetically modified organism (GMO)
- organism whose genome has been artificially changed
- host DNA
- DNA that is present in the genome of the organism of interest
- lysis buffer
- solution to break the cell membrane and release cell contents
- molecular cloning
- cloning of DNA fragments
- multiple cloning site (MCS)
- site that multiple restriction endonucleases can recognize
- Northern blotting
- transfer of RNA from a gel to a nylon membrane
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- technique to amplify DNA
- probe
- small DNA fragment to determine if the complementary sequence is present in a DNA sample
- protease
- enzyme that breaks down proteins
- recombinant DNA
- combining DNA fragments that molecular cloning generates that do not exist in nature; also a chimeric molecule
- recombinant protein
- a gene’s protein product derived by molecular cloning
- reproductive cloning
- entire organism cloning
- restriction endonuclease
- enzyme that can recognize and cleave specific DNA sequences
- reverse genetics
- method of determining the gene’s function by starting with the gene itself instead of starting with the gene product
- reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR)
- PCR technique that involves converting RNA to DNA by reverse transcriptase
- ribonuclease
- enzyme that breaks down RNA
- Southern blotting
- DNA transfer from a gel to a nylon membrane
- Ti plasmid
- plasmid system derived from Agrobacterium tumifaciens that scientists have used to introduce foreign DNA into plant cells
- transgenic
- organism that receives DNA from a different species
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/1-introduction

