Module 11: Rapid Point of Care (POC) Testing
Module 11.5: Heartworm Testing
Heartworm testing
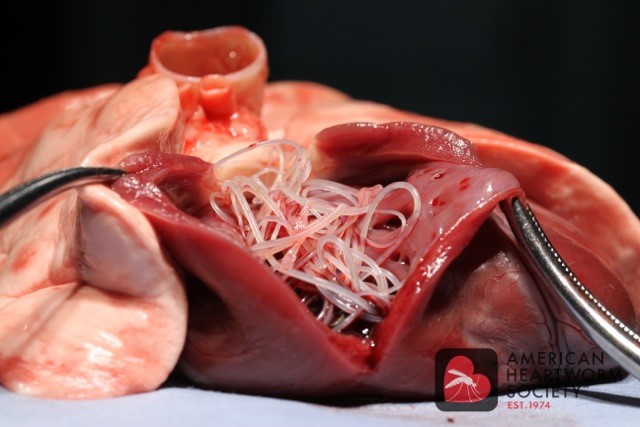
Heartworm disease (HWD) is a mosquito-borne filarial disease that infects dogs and cats worldwide caused by the nematode Dirofilaria immitus. (See Agents of Disease 2 notes for more specifics on the disease and disease presentation) As a result of climate change and the increased movement of both dogs and cats from regions of the United States (and the world) that have a high prevalence of HWD to regions of the country that have traditionally had a low prevalence, HWD has become more widespread. In fact, CAPC has reported an overall 20% increase in HWD prevalence between 2013-2017 for the United States overall, but especially in parts of the country that were considered to have low prevalence.
As HWD becomes more prevalent throughout the United States and worldwide, the need for routine HWD (and other vector-borne diseases) testing will become more common in clinical practice.
Knowledge check
Heartworm ELISA (LFA) testing
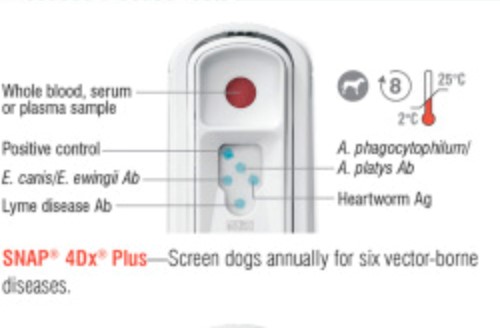
In today’s laboratory, you will be using the IDEXX SNAP 4Dx Plus results to answer the questions in your case study. However, there are several other tests that are available on the market for heartworm screening.
The following chart summarizes the 3 most common LFA tests available on the market for in-clinic testing.
HW test |
Heska SOLO® |
IDEXX SNAP® 4DX Plus |
Zoetis Witness® |
|---|---|---|---|
What sample (s) can you use to run this test (blood, serum, saliva, etc.) |
Plasma, serum, anticoagulated whole blood | Plasma, serum, anticoagulated whole blood | Plasma, serum, anticoagulated whole blood |
What does this test specifically detect? |
Antigen secreted by the adult worm | Antigen secreted by the adult worm | Antigen secreted by the adult worm |
Does this test detect any other diseases? |
No | Anaplasma phagocytophilium (Ab), Anaplasma platys (Ab), Ehrlichia canis (Ab), Ehrlichia ewingii (Antibody), Borellia burgdorferi (Ab), Dirofilaria immitis | No |
Knowledge check
4Dx Plus Procedure
- If stored in a refrigerator, allow all components to equilibrate at room temperature (18–25°C) for 30 minutes before use. Do not heat.
- Using the pipette provided, dispense 3 drops of the patient sample into a new sample tube.
- Holding the bottle vertical, add 4 drops of the conjugate to the sample tube.
- Cap the sample tube and mix it thoroughly by inverting it 3–5 times.
- Place the device on a horizontal surface. Add the entire contents of the sample tube to the sample well, being careful not to splash the contents outside of the sample well. The sample will flow across the result window, reaching the activation circle in 30–60 seconds. Some samples may remain in the sample well.
- When color FIRST appears in the activation circle, push the activator firmly until it is flush with the device’s body.
Note: Some samples may not flow to the activation circle within 60 seconds, and therefore, the circle may not turn color. In this case, press the activator after the sample has flowed across the result window.
- Read the test result at 8 minutes.
Note: The positive control may develop sooner, but results are not complete until 8 minutes.