Module 7: Hematogenous Infectious Disease
Module 7.2: Blood Smear Examples
Blood smear examples
Here are a few examples of common organisms found on the blood film of veterinary patients in the United States:
Organism |
Species found in |
Where it is found (intra/extracellular) |
Magnification easiest found at |
Location on blood smear |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Parasitic |
||||
| Dirofilaria immitus | Canine, Feline | Extracellular | 10x | Feathered edge |
| Trypanosoma sp. | Canine, Bovine | Extracellular | 40x | Monolayer |
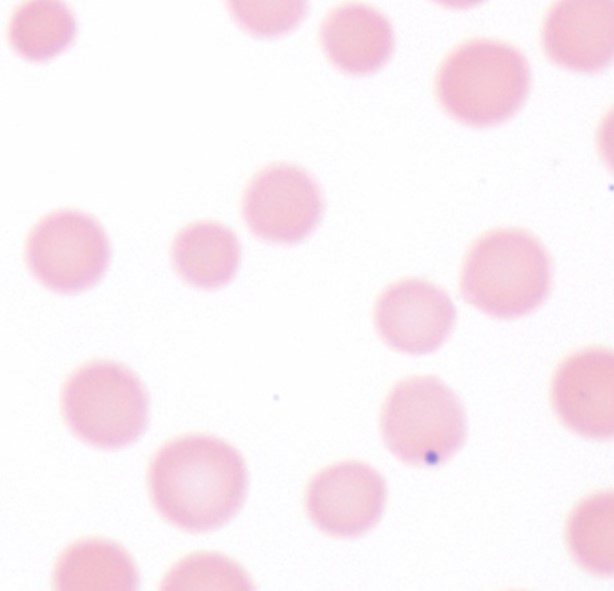
| Babesia sp.* | Canine, bovine | RBC | 40x, 100x | Monolayer |
| Cytauxzoon felis* | Feline | RBC (piroplasms), monocytes (schizonts) | 100x | Monolayer (piroplasms), Feathered edge (schizonts) |
Bacteria |
||||
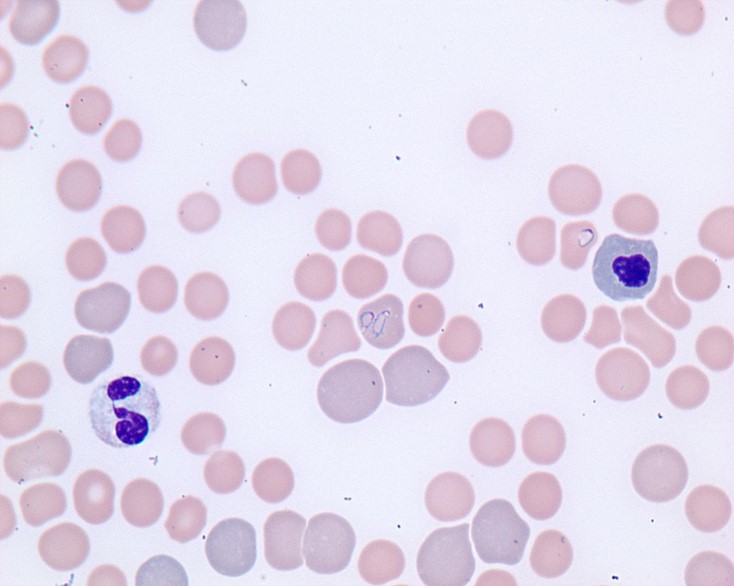
| Anaplasma phagocytophilum | Canine, equine | Neutrophils, eosinophils | 40x | Monolayer |
| Anaplasma marginale* | Bovine | RBC | 40x, 100x | Monolayer |
| Ehrlichia ewingii | Canine | Neutrophils, eosinophils | 40x, 100x | Monolayer |
| Ehrlichia canis | Canine | Monocytes, lymphocytes | 40x, 100x | Monolayer |
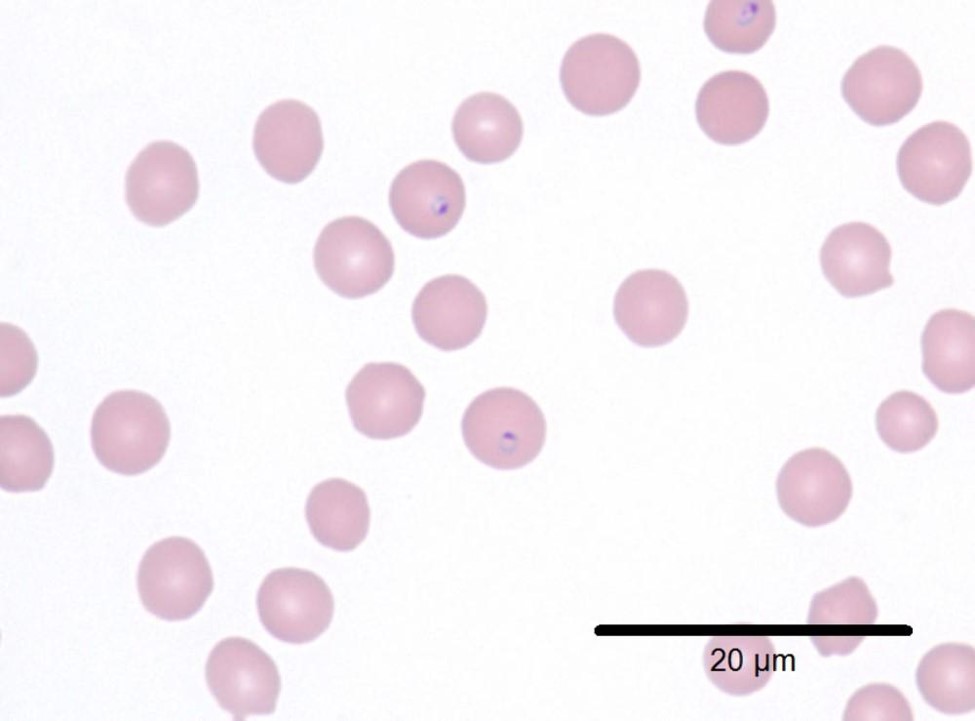
| Mycoplasma sp. (M. haemofelis, M. haemolamae, M. canis) | Canine, feline, camelids, many others | Surface of RBC’s | 100x | Monolayer |
Fungal |
||||
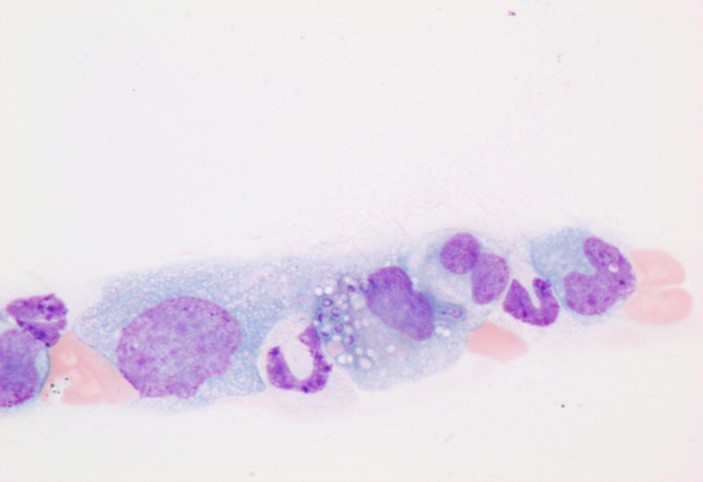
| Histoplasma capsulatum* | Canine | Monocytes | 40x, 100x | Feathered edge, sometimes monolayer |
Visual atlas
Here is a visual atlas of some of the organisms described in the table.